Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Symmetric premixed twin flame#
Simulate two counter-flow jets of premixed reactants shooting into each other. This simulation differs from the similar premixed_counterflow_flame.py example as the latter simulates a jet of reactants shooting into products.
Requires: cantera >= 3.0, matplotlib >= 2.0
An illustration of this configuration is shown in the figure below:
import sys
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import cantera as ct
# Differentiation function for data that has variable grid spacing Used here to
# compute normal strain-rate
def derivative(x, y):
dydx = np.zeros(y.shape, y.dtype.type)
dx = np.diff(x)
dy = np.diff(y)
dydx[0:-1] = dy/dx
dydx[-1] = (y[-1] - y[-2])/(x[-1] - x[-2])
return dydx
def compute_strain_rates(opposed_flame):
# Compute the derivative of axial velocity to obtain normal strain rate
strain_rates = derivative(opposed_flame.grid, opposed_flame.velocity)
# Obtain the location of the max. strain rate upstream of the pre-heat zone.
# This is the characteristic strain rate
max_strain_location = abs(strain_rates).argmax()
min_velocity_point = opposed_flame.velocity[:max_strain_location].argmin()
# Characteristic Strain Rate = K
strain_rate_point = abs(strain_rates[:min_velocity_point]).argmax()
K = abs(strain_rates[strain_rate_point])
return strain_rates, strain_rate_point, K
def compute_consumption_speed(opposed_flame):
Tb = max(opposed_flame.T)
Tu = min(opposed_flame.T)
rho_u = max(opposed_flame.density)
integrand = opposed_flame.heat_release_rate / opposed_flame.cp
total_heat_release = np.trapz(integrand, opposed_flame.grid)
Sc = total_heat_release / (Tb - Tu) / rho_u
return Sc
# This function is called to run the solver
def solve_opposed_flame(opposed_flame, mass_flux=0.12, loglevel=1,
ratio=2, slope=0.3, curve=0.3, prune=0.05):
"""
Execute this function to run the Opposed Flow Simulation. This function
takes a CounterFlowTwinPremixedFlame object as the first argument
"""
opposed_flame.reactants.mdot = mass_flux
opposed_flame.set_refine_criteria(ratio=ratio, slope=slope,
curve=curve, prune=prune)
opposed_flame.show()
opposed_flame.solve(loglevel, auto=True)
# Compute the strain rate, just before the flame. This is not necessarily
# the maximum We use the max. strain rate just upstream of the pre-heat zone
# as this is the strain rate that computations compare against, like when
# plotting Su vs. K
strain_rates, strain_rate_point, K = compute_strain_rates(opposed_flame)
return np.max(opposed_flame.T), K, strain_rate_point
Define parameters#
# Select the reaction mechanism
gas = ct.Solution('gri30.yaml')
# Create a CH4/Air premixed mixture with equivalence ratio=0.75, and at room
# temperature and pressure.
gas.set_equivalence_ratio(0.75, 'CH4', {'O2': 1.0, 'N2': 3.76})
gas.TP = 300, ct.one_atm
# Set the velocity
axial_velocity = 2.0 # in m/s
# Domain half-width of 2.5 cm, meaning the whole domain is 5 cm wide
width = 0.025
Set up the simulation#
# Compute the mass flux, as this is what the Flame object requires
mass_flux = gas.density * axial_velocity # units kg/m2/s
# Create the flame object
opposed_flame = ct.CounterflowTwinPremixedFlame(gas, width=width)
# Uncomment the following line to use a Multi-component formulation. Default is
# mixture-averaged
# opposed_flame.transport_model = 'multicomponent'
Run the solver#
The solver returns the peak temperature, strain rate and the point which we ascribe to the characteristic strain rate.
T, K, strain_rate_point = solve_opposed_flame(opposed_flame, mass_flux, loglevel=1)
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> reactants <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
Mass Flux: 2.268 kg/m^2/s
Temperature: 300 K
Mass Fractions:
O2 0.2232
CH4 0.04197
N2 0.7348
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> flame <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
Pressure: 1.013e+05 Pa
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z velocity spread_rate T lambda eField
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 2 0 300 -2.903e+04 0
0.005 1.6 32 300 -2.903e+04 0
0.01 1.2 64 300 -2.903e+04 0
0.0125 1 80 1110 -2.903e+04 0
0.015 0.8 96 1920 -2.903e+04 0
0.02 0.4 128 1920 -2.903e+04 0
0.025 0 160 1920 -2.903e+04 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z Uo H2 H O O2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0.2232
0.005 0 0 0 0 0.2232
0.01 0 2.06e-21 9.355e-23 1.216e-20 0.2232
0.0125 0 3.711e-06 1.685e-07 2.191e-05 0.1386
0.015 0 7.423e-06 3.37e-07 4.382e-05 0.05402
0.02 0 7.423e-06 3.37e-07 4.382e-05 0.05402
0.025 0 7.423e-06 3.37e-07 4.382e-05 0.05402
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z OH H2O HO2 H2O2 C
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 1.907e-19 2.604e-17 2.619e-22 1.513e-23 1.528e-38
0.0125 0.0003435 0.04691 4.717e-07 2.725e-08 2.753e-23
0.015 0.0006871 0.09382 9.435e-07 5.45e-08 5.506e-23
0.02 0.0006871 0.09382 9.435e-07 5.45e-08 5.506e-23
0.025 0.0006871 0.09382 9.435e-07 5.45e-08 5.506e-23
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z CH CH2 CH2(S) CH3 CH4
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0.04197
0.005 0 0 0 0 0.04197
0.01 1.236e-39 4.048e-39 1.788e-40 3.885e-38 0.04197
0.0125 2.226e-24 7.292e-24 3.22e-25 6.999e-23 0.02098
0.015 4.452e-24 1.458e-23 6.441e-25 1.4e-22 0
0.02 4.452e-24 1.458e-23 6.441e-25 1.4e-22 8.264e-23
0.025 4.452e-24 1.458e-23 6.441e-25 1.4e-22 8.264e-23
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z CO CO2 HCO CH2O CH2OH
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 6.135e-20 3.186e-17 2.588e-28 2.804e-30 6.75e-37
0.0125 0.0001105 0.05739 4.662e-13 5.052e-15 1.216e-21
0.015 0.000221 0.1148 9.324e-13 1.01e-14 2.432e-21
0.02 0.000221 0.1148 9.324e-13 1.01e-14 2.432e-21
0.025 0.000221 0.1148 9.324e-13 1.01e-14 2.432e-21
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z CH3O CH3OH C2H C2H2 C2H3
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 8.315e-39 5.227e-38 9.354e-48 7.624e-45 5.836e-51
0.0125 1.498e-23 9.416e-23 1.685e-32 1.373e-29 1.051e-35
0.015 2.996e-23 1.883e-22 3.37e-32 2.747e-29 2.103e-35
0.02 2.996e-23 1.883e-22 3.37e-32 2.747e-29 2.103e-35
0.025 2.996e-23 1.883e-22 3.37e-32 2.747e-29 2.103e-35
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 HCCO CH2CO
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 9.138e-51 1.002e-56 7.332e-58 2.1e-41 3.353e-41
0.0125 1.646e-35 1.805e-41 1.321e-42 3.783e-26 6.04e-26
0.015 3.292e-35 3.61e-41 2.641e-42 7.566e-26 1.208e-25
0.02 3.292e-35 3.61e-41 2.641e-42 7.566e-26 1.208e-25
0.025 3.292e-35 3.61e-41 2.641e-42 7.566e-26 1.208e-25
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z HCCOH N NH NH2 NH3
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 1.05e-44 3.232e-26 2.797e-27 8.652e-28 3.559e-27
0.0125 1.892e-29 5.822e-11 5.038e-12 1.559e-12 6.411e-12
0.015 3.784e-29 1.164e-10 1.008e-11 3.117e-12 1.282e-11
0.02 3.784e-29 1.164e-10 1.008e-11 3.117e-12 1.282e-11
0.025 3.784e-29 1.164e-10 1.008e-11 3.117e-12 1.282e-11
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z NNH NO NO2 N2O HNO
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 4.476e-27 8.318e-19 1.205e-21 6.697e-23 2.279e-24
0.0125 8.063e-12 0.001498 2.17e-06 1.206e-07 4.106e-09
0.015 1.613e-11 0.002997 4.341e-06 2.413e-07 8.212e-09
0.02 1.613e-11 0.002997 4.341e-06 2.413e-07 8.212e-09
0.025 1.613e-11 0.002997 4.341e-06 2.413e-07 8.212e-09
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z CN HCN H2CN HCNN HCNO
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0 0
0.01 1.185e-33 8.215e-31 1.546e-38 4.735e-42 1.504e-35
0.0125 2.135e-18 1.48e-15 2.785e-23 8.53e-27 2.71e-20
0.015 4.27e-18 2.96e-15 5.57e-23 1.706e-26 5.42e-20
0.02 4.27e-18 2.96e-15 5.57e-23 1.706e-26 5.42e-20
0.025 4.27e-18 2.96e-15 5.57e-23 1.706e-26 5.42e-20
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z HOCN HNCO NCO N2 AR
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0.7348 0
0.005 0 0 0 0.7348 0
0.01 8.599e-31 7.04e-28 1.842e-29 0.7348 0
0.0125 1.549e-15 1.268e-12 3.319e-14 0.7341 0
0.015 3.098e-15 2.536e-12 6.638e-14 0.7334 0
0.02 3.098e-15 2.536e-12 6.638e-14 0.7334 0
0.025 3.098e-15 2.536e-12 6.638e-14 0.7334 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z C3H7 C3H8 CH2CHO CH3CHO
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0
0.005 0 0 0 0
0.01 6.242e-76 4.325e-77 1.343e-47 2.414e-48
0.0125 1.125e-60 7.791e-62 2.42e-32 4.349e-33
0.015 2.249e-60 1.558e-61 4.84e-32 8.697e-33
0.02 2.249e-60 1.558e-61 4.84e-32 8.697e-33
0.025 2.249e-60 1.558e-61 4.84e-32 8.697e-33
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> products <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
z
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0
************ Solving on 7 point grid with energy equation enabled ************
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 2.848e-05 log(ss)= 5.887
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0004865 log(ss)= 5.15
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.008313 log(ss)= 2.394
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [7] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
grid refinement disabled.
******************** Solving with grid refinement enabled ********************
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [7] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 1 2 3 4 5
to resolve C2H2 C2H4 C2H6 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 1 point 4 spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001139 log(ss)= 5.74
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.002919 log(ss)= 3.658
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [12] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 2 point 7 spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001139 log(ss)= 5.709
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 6.082e-05 log(ss)= 5.226
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001155 log(ss)= 5.842
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [20] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 1 4 9 10 11 12 13 17 18
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 1 point 4 spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001139 log(ss)= 5.674
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [29] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 0 10 14 15 16 17 18 23 26 27
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 0 point 10 point 23 spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 7.594e-05 log(ss)= 6.126
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 6.407e-05 log(ss)= 6.245
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 9.123e-05 log(ss)= 6.094
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 3.849e-05 log(ss)= 6.401
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0004384 log(ss)= 5.118
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [39] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 24 25 26 27 28 36 37
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.01484375
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 7.594e-05 log(ss)= 6.226
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 5.406e-05 log(ss)= 5.867
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0004105 log(ss)= 4.915
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [45] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H7 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.01703125
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001139 log(ss)= 5.821
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 5.406e-05 log(ss)= 6.22
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0009237 log(ss)= 4.454
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [51] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H7 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T spread_rate velocity
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.01734375
refine: discarding point at 0.017656250000000002
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001709 log(ss)= 5.757
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 7.208e-05 log(ss)= 5.962
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0008211 log(ss)= 4.793
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [56] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 29 34 39 40 41 42 43 44
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H7 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 N2O NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 29 point 34 velocity
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.017968750000000002
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0001139 log(ss)= 5.601
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.000865 log(ss)= 4.844
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [63] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
to resolve C C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H7 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCCOH HCN HCO HNCO HO2 N2 NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 46 velocity
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.018437500000000002
refine: discarding point at 0.018750000000000003
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.0002563 log(ss)= 5.459
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve failed.
Attempt 10 timesteps.
Final timestep info: dt= 0.001946 log(ss)= 4.443
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [69] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 42 51 52 53 54 55 56 57
to resolve C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H7 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO CO2 H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCCOH HCN HCNO HCO HNCO HO2 N2 NO NO2 O O2 OH T point 42 point 53 velocity
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.018281250000000002
refine: discarding point at 0.018593750000000003
refine: discarding point at 0.018906250000000003
refine: discarding point at 0.019218750000000003
refine: discarding point at 0.019687500000000004
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [72] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59
to resolve C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H7 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CHO CH2CO CH2O CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O CH3OH CH4 CO H H2 H2O H2O2 HCCO HCCOH HCN HCO HO2 N2 NO2 O O2 OH T point 59
##############################################################################
refine: discarding point at 0.019531250000000003
refine: discarding point at 0.019921875000000006
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [80] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 47 48 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59
to resolve C2H2 C2H3 C2H4 C2H5 C2H6 C3H8 CH CH2 CH2(S) CH2CO CH2OH CH3 CH3CHO CH3O HCCO HCO
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [90] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 43 44 45 46 48 52 53
to resolve C2H6 C3H8 CH3O NO2 point 48
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [97] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
##############################################################################
Refining grid in flame.
New points inserted after grid points 46
to resolve point 46
##############################################################################
..............................................................................
Attempt Newton solution of steady-state problem.
Newton steady-state solve succeeded.
Problem solved on [98] point grid(s).
..............................................................................
no new points needed in flame
Compute flame properties#
You can plot/see all state space variables by calling opposed_flame.foo, where
foo is T, Y[i], and so forth. The spatial variable (distance in meters) is in
opposed_flame.grid. Thus to plot temperature vs distance, use opposed_flame.grid`
and opposed_flame.T.
Sc = compute_consumption_speed(opposed_flame)
if "native" in ct.hdf_support():
output = Path() / "premixed_counterflow_twin_flame.h5"
else:
output = Path() / "premixed_counterflow_twin_flame.yaml"
output.unlink(missing_ok=True)
opposed_flame.save(output, name="mix")
print(f"Peak temperature: {T:.1f} K")
print(f"Strain Rate: {K:.1f} 1/s")
print(f"Consumption Speed: {Sc * 100:.2f} cm/s")
opposed_flame.save("premixed_counterflow_twin_flame.csv", basis="mole", overwrite=True)
/home/runner/work/cantera/cantera/build/doc/samples/python/onedim/premixed_counterflow_twin_flame.py:66: DeprecationWarning: `trapz` is deprecated. Use `trapezoid` instead, or one of the numerical integration functions in `scipy.integrate`.
total_heat_release = np.trapz(integrand, opposed_flame.grid)
Peak temperature: 1919.5 K
Strain Rate: 163.7 1/s
Consumption Speed: 20.96 cm/s
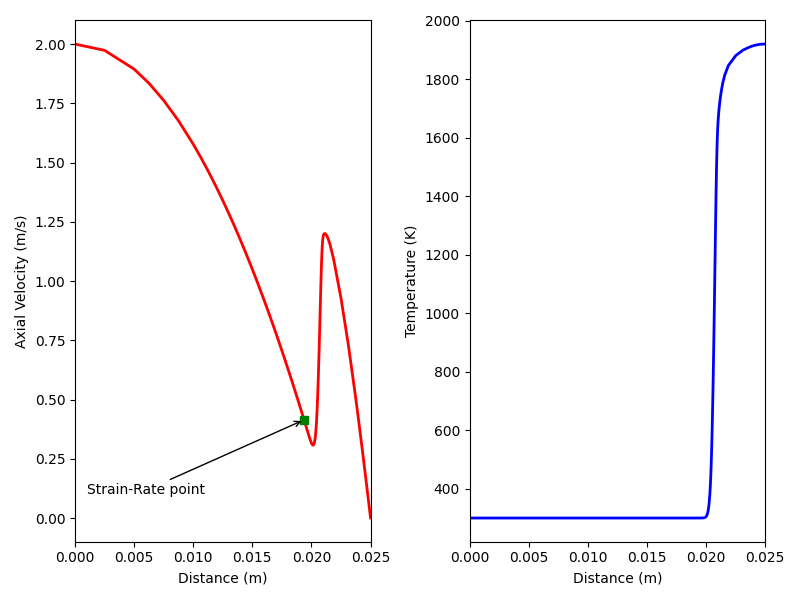
Plot results#
Generate plots to see results, if desired.
if '--plot' in sys.argv:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), facecolor='white')
# Axial Velocity Plot
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(opposed_flame.grid, opposed_flame.velocity, 'r', lw=2)
plt.xlim(opposed_flame.grid[0], opposed_flame.grid[-1])
plt.xlabel('Distance (m)')
plt.ylabel('Axial Velocity (m/s)')
# Identify the point where the strain rate is calculated
plt.plot(opposed_flame.grid[strain_rate_point],
opposed_flame.velocity[strain_rate_point], 'gs')
plt.annotate('Strain-Rate point',
xy=(opposed_flame.grid[strain_rate_point],
opposed_flame.velocity[strain_rate_point]),
xytext=(0.001, 0.1),
arrowprops={'arrowstyle': '->'})
# Temperature Plot
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(opposed_flame.grid, opposed_flame.T, 'b', lw=2)
plt.xlim(opposed_flame.grid[0], opposed_flame.grid[-1])
plt.xlabel('Distance (m)')
plt.ylabel('Temperature (K)')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
print('************')
print('Plotting option not enabled. Re-run script with --plot to see key plots.')
print('************')
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 2.634 seconds)

